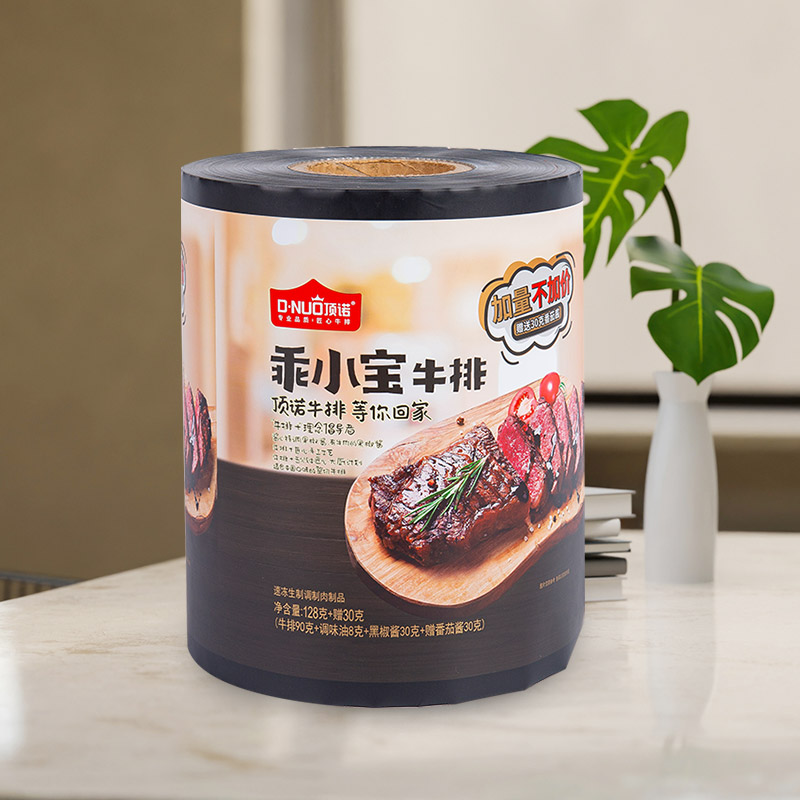
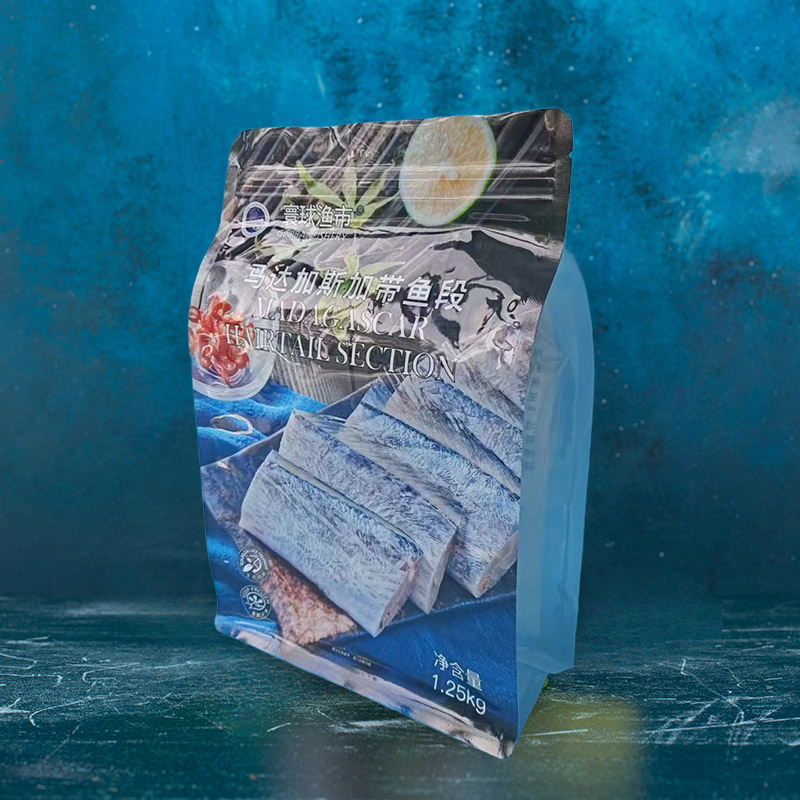
Thermoforming is a widely used manufacturing process where a plastic sheet or film is heated until pliable, then shaped over a mold to create various packaging containers and products. This technique is especially popular in packaging due to its cost-effectiveness, design flexibility, and high production speed. From food trays and blister packs to medical device containers, thermoforming offers diverse applications across multiple industries.
Central to successful thermoforming packaging is the use of specialized thermoforming films. These films must withstand the forming process while delivering specific performance characteristics such as strength, clarity, and barrier protection. As consumer demand grows for fresh, safe, and longer-lasting products, the need for advanced packaging solutions becomes critical.
This demand has driven innovation in high barrier and multi-layer films, which combine multiple materials into one co-extruded structure. Multi-layer co-extruded films provide enhanced protection against oxygen, moisture, light, and other external factors that can compromise product quality. Their tailored properties enable extended shelf life, reduce food waste, and support premium packaging aesthetics.
In this article, we will explore the nature and advantages of multi-layer co-extruded thermoforming films, their role in packaging, and the latest trends shaping this dynamic industry.

Content
- 1 What is Thermoforming Film?
- 2 Understanding High Barrier Thermoforming Film
- 3 Multi-Layer Co-Extruded Films: A Deeper Dive
- 4 Bottom Thermoforming Film: Specific Applications
- 5 Advantages of High Barrier Film Packaging
- 6 Applications of Thermoforming Films
- 7 Choosing the Right Thermoforming Film
- 8 Trends and Innovations in Thermoforming Films
- 9 Conclusion
What is Thermoforming Film?
Thermoforming film is a type of plastic film specifically designed to undergo the thermoforming process, where it is heated and shaped into containers or trays. These films possess characteristics that allow them to soften without degrading, enabling them to conform precisely to molds while maintaining structural integrity.
The thermoforming process typically involves heating a plastic sheet or film to its forming temperature, then stretching it over or into a mold using vacuum, pressure, or mechanical means. Once cooled, the formed shape retains its configuration, ready for filling and sealing. This process supports high-speed, cost-efficient production of packaging with complex shapes and designs.
Thermoforming films come in various types based on their rigidity:
Rigid films: Thick and sturdy, suitable for products requiring firm protection and shape retention.
Semi-rigid films: Balance flexibility with strength, often used in applications needing moderate protection and easy handling.
Flexible films: Thin and pliable, used primarily for sealing or as part of multi-layer structures rather than forming strong shapes.
Each type of film can be engineered with specific properties to suit the intended packaging application, including clarity, barrier resistance, heat sealability, and printability.
Understanding High Barrier Thermoforming Film
In the context of thermoforming films, "high barrier" refers to the film’s ability to prevent or significantly reduce the transmission of gases, moisture, and sometimes light. These barrier properties are essential for protecting sensitive products from spoilage, contamination, or degradation.
Key barrier attributes include:
Oxygen barrier: Prevents oxygen from entering the package, which can cause oxidation and spoilage of food and pharmaceuticals.
Moisture barrier: Limits water vapor transmission to maintain product texture and prevent microbial growth.
Light barrier: Shields products from UV or visible light that may degrade nutrients, flavors, or colors.
To achieve these barrier functions, high barrier thermoforming films incorporate specialized materials such as:
EVOH (Ethylene Vinyl Alcohol): Offers excellent oxygen barrier performance while maintaining clarity.
PVDC (Polyvinylidene Chloride): Provides superior moisture and oxygen resistance but with some environmental concerns.
Aluminum Foil Layers: Deliver outstanding barriers to oxygen, moisture, and light, commonly used in pharmaceutical and premium food packaging.
High barrier films are critical in packaging applications where product freshness and safety are paramount. This includes perishable foods like meat, cheese, and ready-to-eat meals, as well as sensitive pharmaceuticals that require extended shelf life and contamination prevention.
Multi-Layer Co-Extruded Films: A Deeper Dive
Multi-layer co-extruded films are produced by simultaneously extruding several layers of different polymers through a single die to form a unified film structure. This co-extrusion process enables the combination of multiple materials with diverse properties into one film, enhancing overall performance beyond what a single-layer film can provide.
The benefits of multi-layer co-extrusion include:
Combining functional properties: Different layers can provide barrier protection, mechanical strength, sealability, printability, or flexibility, tailored to the needs of the packaged product.
Cost-effectiveness: Using a mix of high-performance and economical materials optimizes costs while achieving desired film functions.
Design flexibility: Layer thicknesses and compositions can be adjusted to meet specific performance and regulatory requirements.
Common multi-layer film structures typically include:
Outer layers: Provide mechanical strength, printability, and moisture resistance (often made from polypropylene (PP), polyethylene (PE), or polyester (PET)).
Barrier layers: Such as EVOH or PVDC, which block oxygen and other gases.
Tie layers: Specialized adhesive resins that bond incompatible polymers together.
Sealant layers: Ensure heat sealability, commonly made of PE or modified PE.
For example, a typical 5-layer co-extruded film might have an outer PET layer for durability and printability, a middle EVOH layer for oxygen barrier, and inner PE layers for sealability and moisture resistance.
This multi-layer approach delivers films that meet stringent packaging demands in food, pharmaceutical, and industrial applications, making co-extruded films a versatile and widely adopted solution.
Bottom Thermoforming Film: Specific Applications
Bottom thermoforming film is the lower web of a thermoformed packaging system. During the forming process, this film is heated and shaped into a tray or cavity that holds the product. It plays a vital role in both the structure and protection of the packaged item, making its material selection and performance characteristics crucial.
What Makes Bottom Film Unique?
Unlike top lidding films, which are often flat and focused on sealing or printing, bottom thermoforming films must possess the strength, formability, and barrier properties needed to create the actual container. These films must withstand mechanical stress during forming, resist punctures, and maintain their integrity during filling, sealing, storage, and transportation.
Common Materials for Bottom Thermoforming Films
Depending on the application, bottom films are engineered from various materials, including:
Polypropylene (PP): Offers good clarity, high heat resistance, and durability, making it suitable for microwaveable or hot-fill applications.
Polyethylene (PE): Known for its flexibility, impact resistance, and excellent sealing properties. Often used in conjunction with other materials.
Polyamide (PA or Nylon): Provides high strength and excellent formability. Often used in multi-layer films to reinforce mechanical integrity.
EVOH: Integrated as a barrier layer to protect against oxygen transmission, especially in vacuum or MAP (modified atmosphere packaging) systems.
These materials are often co-extruded into multi-layer structures to deliver a balance of strength, flexibility, and barrier performance tailored to specific product needs.
Specific Applications of Bottom Thermoforming Films
Bottom thermoforming films are widely used in food and non-food sectors. Key applications include:
Meat and Poultry Packaging: Films are designed to provide strong oxygen and moisture barriers to preserve freshness and color, especially under vacuum sealing or MAP.
Cheese Packaging: High barrier bottom films prevent moisture loss and oxygen ingress, helping extend shelf life and retain flavor.
Seafood Packaging: Films are selected for resistance to punctures and water vapor to keep seafood fresh and securely contained.
Ready Meals: Used in dual-ovenable or microwave-safe trays for consumer convenience.
Medical Devices: Films used for sterile blister packs must offer clean forming, protection, and compatibility with sterilization methods.
Selecting the right bottom thermoforming film is crucial for ensuring package performance, maintaining product safety, and meeting branding or regulatory requirements.
Advantages of High Barrier Film Packaging
High barrier thermoforming films play a critical role in preserving product integrity, safety, and shelf appeal. Their advanced performance characteristics offer a wide range of benefits across industries, particularly in food, pharmaceutical, and healthcare packaging.
1. Extended Shelf Life
One of the primary advantages of high barrier films is their ability to significantly extend the shelf life of packaged products. By preventing oxygen and moisture ingress, these films reduce spoilage, inhibit microbial growth, and maintain the freshness, color, and taste of perishable goods. This is especially important in vacuum-sealed and modified atmosphere packaging systems used for meat, dairy, and ready-to-eat meals.
2. Enhanced Product Protection
High barrier films offer excellent protection against external elements such as air, humidity, light, and contaminants. This is crucial for products that are sensitive to environmental changes, including pharmaceuticals, electronic components, and medical devices. By forming a stable, protective environment, the films ensure that the product reaches the end user in optimal condition.
3. Reduced Food Waste
By prolonging freshness and preventing premature spoilage, high barrier films contribute to reducing food waste across the supply chain. Products last longer on store shelves and in consumers’ homes, supporting sustainability goals and minimizing economic losses for manufacturers and retailers.
4. Improved Aesthetics and Branding Opportunities
Multi-layer co-extruded films can be engineered for clarity, gloss, printability, and formability—enhancing the visual appeal of the packaging. This allows brands to showcase their products attractively while maintaining the functionality and durability required for protection and transportation.
5. Compliance with Industry Regulations
In food and pharmaceutical packaging, meeting strict regulatory standards is non-negotiable. High barrier films are often developed to comply with safety guidelines related to material composition, barrier performance, and sterilization compatibility. This makes them suitable for use in regulated environments such as food production facilities, hospitals, and pharmaceutical packaging lines.
Applications of Thermoforming Films
Thermoforming films serve as a foundational element in a wide variety of packaging solutions, offering protection, presentation, and performance across multiple sectors. Their ability to be formed into customized shapes and integrated with barrier and sealing technologies makes them highly adaptable to diverse product needs.
Food Packaging
Thermoforming films are extensively used in the food industry due to their excellent preservation capabilities and visual presentation.
Meat and Poultry: These perishable items require vacuum or MAP packaging using high barrier films to inhibit bacterial growth, retain color, and prevent dehydration. The formability of the bottom film ensures a snug fit, while top films maintain seal integrity.
Cheese and Dairy Products: Cheese packaging often relies on multi-layer films with moisture and oxygen barriers to prevent mold and flavor loss, enabling longer storage without refrigeration fluctuations affecting quality.
Fruits and Vegetables: Films with breathable properties or selective barrier layers are used to maintain freshness, reduce spoilage, and accommodate modified atmosphere requirements.
Ready-to-Eat Meals: Dual-ovenable and microwave-safe thermoformed trays provide both functionality and convenience, allowing food to be stored, heated, and served in a single package.
Medical Packaging
Precision, hygiene, and barrier performance are essential in healthcare packaging. Thermoforming films are used to protect sensitive products during transport and storage, while also supporting sterilization processes.
Pharmaceuticals: Unit-dose blister packs for tablets and capsules rely on thermoforming films with high moisture and oxygen resistance to maintain drug stability and shelf life.
Medical Devices: Syringes, catheters, and diagnostic tools are often sealed in thermoformed trays made of rigid or semi-rigid film structures that can be sterilized via radiation, ethylene oxide, or steam.
Surgical Instruments: Packaging for instruments requires puncture-resistant films that hold the product firmly while maintaining sterility.
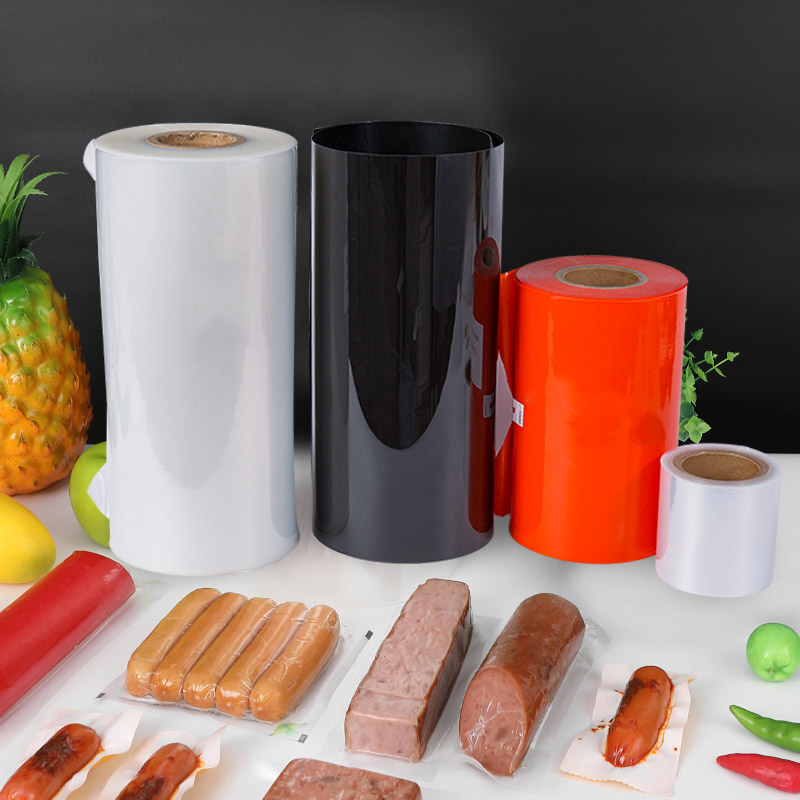

Industrial Packaging
In the industrial sector, thermoforming films provide robust, form-fitting packaging solutions that protect products during long-distance transport or extended storage.
Electronics: Films are used to form anti-static or ESD-safe packaging for circuit boards, chips, and small components that require protection from moisture and electrostatic discharge.
Automotive Parts: Packaging for small, high-precision components often uses customized trays formed from durable, static-free thermoforming films.
Consumer Goods: High-impact packaging for tools, batteries, and electronics uses semi-rigid or rigid thermoformed blisters to balance product visibility with protection.
Thermoforming films continue to evolve in each of these application areas, driven by changing product requirements, stricter safety standards, and demand for sustainable packaging solutions.
Thermoforming films serve as a foundational element in a wide variety of packaging solutions, offering protection, presentation, and performance across multiple sectors. Their ability to be formed into customized shapes and integrated with barrier and sealing technologies makes them highly adaptable to diverse product needs.
Food Packaging
Thermoforming films are extensively used in the food industry due to their excellent preservation capabilities and visual presentation.
Meat and Poultry: These perishable items require vacuum or MAP packaging using high barrier films to inhibit bacterial growth, retain color, and prevent dehydration. The formability of the bottom film ensures a snug fit, while top films maintain seal integrity.
Cheese and Dairy Products: Cheese packaging often relies on multi-layer films with moisture and oxygen barriers to prevent mold and flavor loss, enabling longer storage without refrigeration fluctuations affecting quality.
Fruits and Vegetables: Films with breathable properties or selective barrier layers are used to maintain freshness, reduce spoilage, and accommodate modified atmosphere requirements.
Ready-to-Eat Meals: Dual-ovenable and microwave-safe thermoformed trays provide both functionality and convenience, allowing food to be stored, heated, and served in a single package.
Medical Packaging
Precision, hygiene, and barrier performance are essential in healthcare packaging. Thermoforming films are used to protect sensitive products during transport and storage, while also supporting sterilization processes.
Pharmaceuticals: Unit-dose blister packs for tablets and capsules rely on thermoforming films with high moisture and oxygen resistance to maintain drug stability and shelf life.
Medical Devices: Syringes, catheters, and diagnostic tools are often sealed in thermoformed trays made of rigid or semi-rigid film structures that can be sterilized via radiation, ethylene oxide, or steam.
Surgical Instruments: Packaging for instruments requires puncture-resistant films that hold the product firmly while maintaining sterility.
Industrial Packaging
In the industrial sector, thermoforming films provide robust, form-fitting packaging solutions that protect products during long-distance transport or extended storage.
Electronics: Films are used to form anti-static or ESD-safe packaging for circuit boards, chips, and small components that require protection from moisture and electrostatic discharge.
Automotive Parts: Packaging for small, high-precision components often uses customized trays formed from durable, static-free thermoforming films.
Consumer Goods: High-impact packaging for tools, batteries, and electronics uses semi-rigid or rigid thermoformed blisters to balance product visibility with protection.
Thermoforming films continue to evolve in each of these application areas, driven by changing product requirements, stricter safety standards, and demand for sustainable packaging solutions.
Choosing the Right Thermoforming Film
Selecting the appropriate thermoforming film for your application involves a careful evaluation of product needs, processing methods, cost constraints, and environmental considerations. Each application has unique requirements, and the film must be tailored to ensure optimal performance and efficiency.
Factors to Consider When Selecting a Thermoforming Film
1. Product Requirements
Barrier Properties: Assess the product's sensitivity to oxygen, moisture, and light. High-fat or protein-rich foods like meat and cheese need strong oxygen barriers, while pharmaceuticals may require both moisture and light protection.
Mechanical Strength: Products with sharp edges or irregular shapes may require puncture-resistant or reinforced films to avoid damage during packaging and transit.
Temperature Resistance: Consider whether the film will undergo heat sealing, sterilization, refrigeration, or freezing. Materials like PP offer high heat resistance, while PE is more suitable for cold storage.
2. Thermoforming Process Compatibility
Forming Depth and Complexity: Deeper cavities or detailed shapes demand films with excellent formability, such as those containing PA (nylon) for added stretch and strength.
Top Film Compatibility: Ensure sealing compatibility between bottom and top films, especially when using multilayer structures with different sealing layers.
Production Speed: Films should match your machine’s forming and sealing capabilities to maintain efficiency without compromising performance.
3. Cost Considerations
Material Selection: Multi-layer co-extruded films allow for strategic use of expensive barrier materials only where needed, helping balance cost and performance.
Waste Minimization: Films with high formability can reduce scrap rates during production and lower the total cost of packaging per unit.
Storage and Logistics: Lighter or thinner films can reduce storage and shipping costs, provided they still meet protective requirements.
4. Sustainability Goals
Recyclability: Some single-material films (like mono-PP or mono-PE) are easier to recycle, supporting eco-friendly initiatives.
Bio-based Options: For brands focused on reducing carbon footprint, bio-based or compostable films are becoming more available in thermoforming applications.
Reduced Material Usage: Advances in material strength allow for downgauging—using thinner films without sacrificing performance.
Questions to Ask Your Film Supplier
What barrier properties does the film offer, and how are they measured?
Is the film compatible with my current thermoforming equipment and sealing system?
Can the film be used in contact with food or pharmaceutical products under relevant regulations?
Are there sustainable alternatives with similar performance?
What are the lead times and customization options for film thickness, width, and structure?
Choosing the right thermoforming film is not just a technical decision—it directly impacts product quality, operational efficiency, brand image, and regulatory compliance.
Trends and Innovations in Thermoforming Films
The thermoforming film industry continues to evolve, driven by market demands for sustainability, improved performance, regulatory compliance, and consumer convenience. Manufacturers are investing in advanced materials and processes to meet these expectations while maintaining cost-efficiency and packaging functionality.
1. Sustainable and Bio-Based Films
Environmental concerns are reshaping the packaging landscape, with strong demand for recyclable, compostable, and renewable material solutions. In response, manufacturers are:
Developing mono-material films (e.g., all-PE or all-PP structures) that are easier to recycle within existing waste management systems.
Introducing bio-based polymers, such as PLA (polylactic acid), which are derived from renewable resources and offer compostability under industrial conditions.
Exploring downgauging strategies that reduce material usage without compromising performance, helping to cut down on plastic waste and production costs.
Sustainability is not just a trend—it’s becoming a key selection criterion, especially for brands positioning themselves as environmentally responsible.
2. Improved Barrier Technologies
Emerging applications and longer global supply chains demand better product protection. Innovations include:
Enhanced EVOH formulations for better oxygen resistance at reduced thickness.
Alternative barrier coatings, such as silicon oxide or aluminum oxide, applied in thin layers to maintain transparency while providing high barrier performance.
Reinforced multilayer designs, which offer superior puncture resistance, seal strength, and product safety in harsh distribution environments.
These developments ensure products stay fresh and intact for extended periods, even under challenging storage or transport conditions.
3. Advanced Co-Extrusion Techniques
New multi-layer extrusion technologies enable the creation of films with 7, 9, or even 11 layers, each fine-tuned for a specific function. These advancements allow for:
Optimized layer distribution, balancing cost with performance.
Use of functional additives, such as anti-fog agents, slip modifiers, or antimicrobial compounds.
Custom-engineered solutions for unique forming requirements or regulatory demands.
As co-extrusion equipment becomes more sophisticated, manufacturers can create thinner, more complex films with precision control over properties.
4. Smart Packaging Solutions
Innovation is extending beyond physical protection into intelligent packaging that interacts with consumers or supply chains. Smart packaging options being explored include:
QR codes and NFC tags, enabling product traceability, authentication, and consumer engagement.
Time-temperature indicators (TTIs) integrated into films to monitor product freshness or cold chain compliance.
Oxygen scavengers or moisture absorbers built into the film to actively protect sensitive products.
Though still in early stages for mass adoption in thermoforming applications, these smart features are poised to transform packaging into a data-driven tool.
Conclusion
Thermoforming films, especially high barrier and multi-layer co-extruded types, have become a cornerstone of modern packaging. Their ability to protect, preserve, and present products across a wide range of industries—particularly food, medical, and industrial sectors—makes them indispensable in today’s market.
Multi-layer co-extruded films deliver a balanced combination of properties by layering different materials to achieve superior barrier performance, mechanical strength, and cost-efficiency. They are highly customizable, enabling packaging solutions tailored to the unique needs of each product, from oxygen-sensitive foods to sterile medical instruments.
Choosing the right thermoforming film is a strategic decision. It requires evaluating product requirements, processing conditions, cost considerations, and long-term sustainability goals. Working closely with knowledgeable suppliers ensures that you can navigate these choices effectively and deploy a film that performs reliably throughout the product’s lifecycle.
As market demands evolve, innovation in thermoforming film technology continues to accelerate. Developments in bio-based materials, recyclable structures, and smart packaging are shaping the future of this sector—offering both functional performance and environmental responsibility.
For businesses aiming to improve product protection, extend shelf life, and align with sustainability initiatives, advanced thermoforming films—especially high barrier, multi-layer co-extruded options—offer a forward-looking packaging solution with measurable value.

 EN
EN
 English
English 日本語
日本語 Español
Español Deutsch
Deutsch عربى
عربى